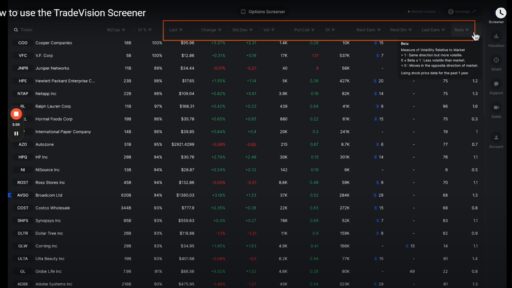
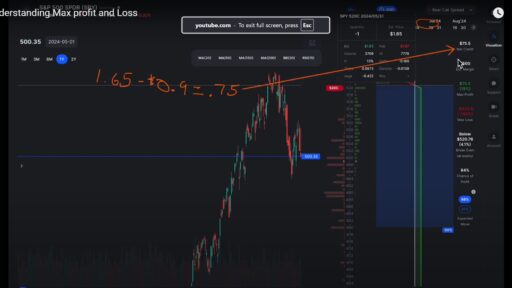
In the world of options trading, the strategies you employ can significantly impact your overall profitability. One of the most effective approaches is to focus on selling options rather than buying them. This strategy not only allows for greater flexibility but also provides a buffer against market fluctuations. Let’s dive into the rationale behind this approach and explore the ideal market conditions for selling options.
The Advantages of Selling Options
Built-In Buffer with Out-of-the-Money Strikes
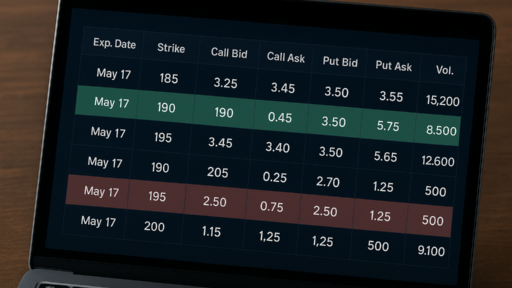
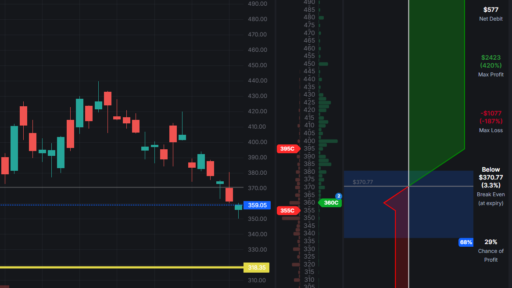
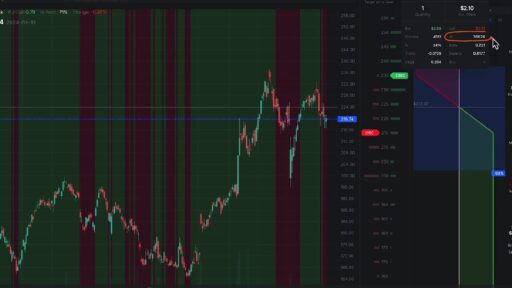
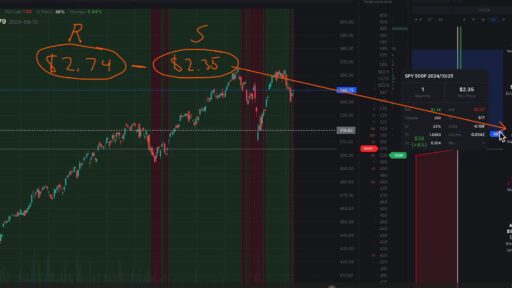
When you sell options, particularly when you position your brief strikes out-of-the-money, you create a buffer that enhances your chances of profitability. This means that the underlying asset can move against you to a certain extent, and you can still emerge profitable. This buffer is especially beneficial in volatile markets, where price movements can be erratic.
Directional Independence
As a seller of options, you are not required to be directionally correct. This flexibility is a significant advantage compared to buying options, where you need to predict the asset’s direction accurately to make a profit. While there are rare cases where long options can yield a profit without a correct directional move, these are exceptions rather than the rule.
Ideal Market Conditions for Selling options
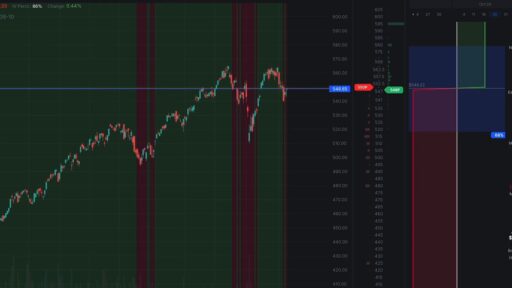
The optimal environment for selling options is characterized by high implied volatility. Historical data indicates that volatility tends to be mean-reverting, meaning that when it is high, it usually decreases over time. By selling options in a high-volatility environment, you can capitalize on the subsequent compression of implied volatility, increasing your potential profits as the market stabilizes.
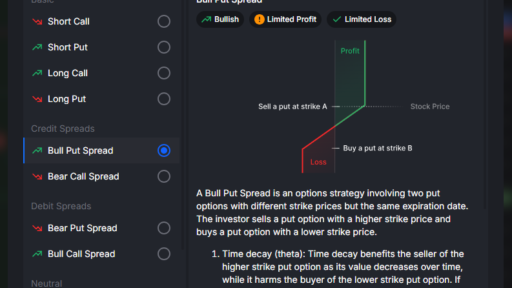
The Case for Long Spreads
While selling options should generally be your default strategy, incorporating long spreads can be beneficial, particularly in low-volatility environments. When volatility is low, options are cheaper, allowing you to establish long positions with lower costs. If volatility does increase, you stand to benefit from this shift.
What About Buying Options?
You might wonder if there are ever circumstances where buying options is advisable. While outright long options (like long calls or puts) are usually not recommended due to the decay associated with negative theta, purchasing long spreads can be a strategic move.
In low-volatility conditions, options prices tend to be more favorable, making it an opportune time to consider long strategies. Should volatility subsequently increase, your long positions can gain value as the market shifts.
Conclusion
As an options trader, adopting a mindset focused on selling options can provide you with several advantages, including a built-in buffer against adverse movements and reduced reliance on directional accuracy. By strategically placing your brief strikes out-of-the-money and recognizing the ideal market conditions for selling—especially during periods of high volatility—you can significantly enhance your trading portfolio.
While selling options should generally be your primary approach, don’t overlook the potential benefits of buying long spreads in low-volatility scenarios. This balanced strategy allows you to navigate the complexities of the market effectively, increasing your chances of long-term success