Have you ever tasted vanilla ice cream? Its classic flavor serves as the perfect basis for a myriad of toppings and mix-ins. On a hot summer day, when you are five and happy, you don’t need anything more than this creamy texture and feeling of being refreshed.
This dessert is truly a testament to how minimal ingredients can create something extraordinary.
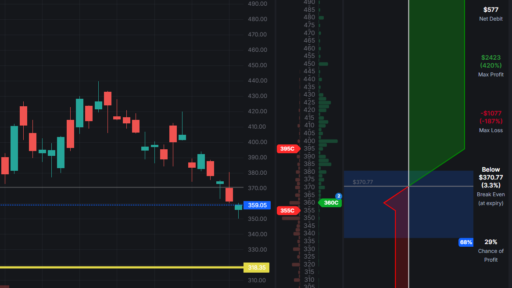
Image 1 – Simply Fabulous
The trading journey is almost like growing up again. You are learning to walk, talk, and understand basic concepts. You start to control your emotions, generate your long-term vision over the immediate gratification…
And suddenly there it is. Your’s truly
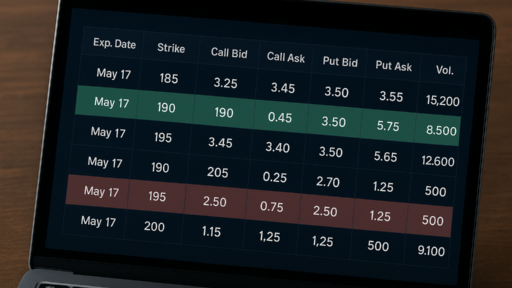
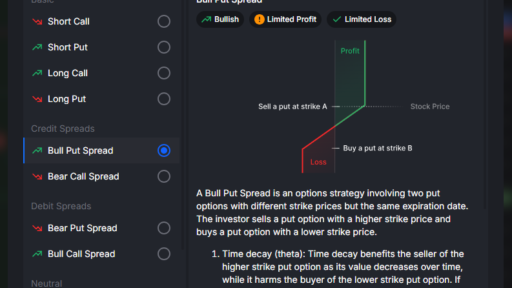
Plain Vanilla Option Ice Cream
And it is as tasty as heaven above. To simplify all the definitions granted:
- It is tasty. A good entry price option contract can be incredibly profitable on the strike date and on the way to it.
- It is cheap. You don’t need to pay in full, just a “Premium”, or even get more money holding it as a contract (we will see into this opportunity later)
- It saves your tender belly. Hedge your stock portfolio with the Vanilla Option whenever you need to be sure the market won’t eat you alive.
And the most Vanilla Option is the European Option.
European Option
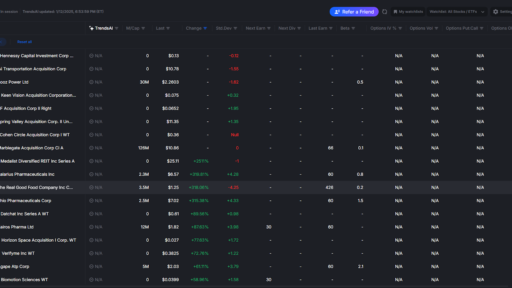
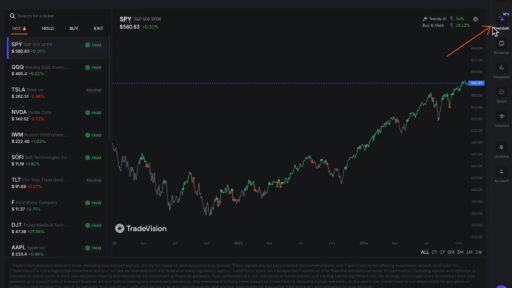
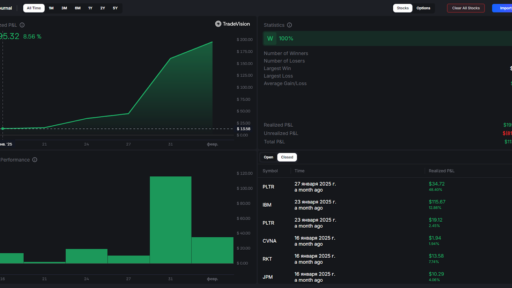
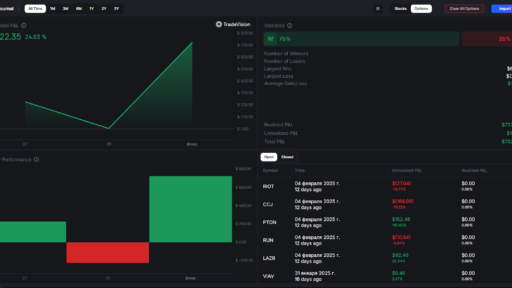
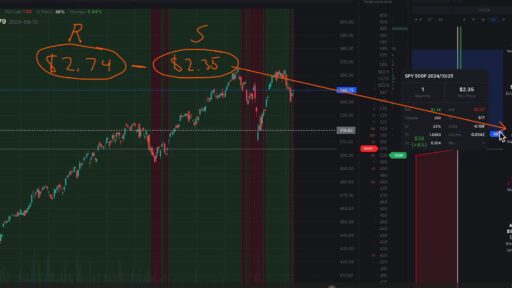
Image 2 – Use the option trading wisely and start a day with such a view
European Options: A Specific Type of Option
A European option is a special kind of option where you can only use it on the expiration date—not before. For example, if you buy a European call option to buy a stock, you can only exercise that option (use it to buy the stock) on the exact expiration date, no matter what happens to the stock price before then.
Options in the Real World: Currency Exchange
Options aren’t just for stocks — they can also be used for currencies. For example, imagine you’re a business owner who needs to exchange US Dollars (USD) for Euros (EUR). The exchange rate between these currencies can change daily, which makes planning tricky. This is where an FX option (short for foreign exchange option) comes in. It gives you the right to exchange one currency for another at a specific rate on a specific date.
Why Use Options?
Options can be used for two main purposes:
- Insurance: Just like you buy car insurance to protect yourself from accidents, you can use options to protect yourself from bad market moves.
- Speculation: Some people use options to bet on whether a stock or currency will go up or down in price.
Let’s look at two examples to see how this works in real life.
Example 1: Nancy’s Bakery Business
Nancy runs a successful pastry business in the US. She’s expanding to France, where customers pay in Euros (EUR). But Nancy’s costs—like paying her employees and rent—are in US Dollars (USD). This creates a problem: if the exchange rate between USD and EUR changes, Nancy could lose money when she converts her Euros back to Dollars.
To protect herself, Nancy buys a call option on the USD/EUR exchange rate. Here’s how it works:
- If the exchange rate gets worse (meaning it costs more USD to buy EUR), Nancy can use her option to exchange Euros at a better rate.
- If the exchange rate stays the same or improves, Nancy doesn’t have to use the option. She can just exchange her Euros at the current rate.
This way, Nancy is protected if the exchange rate moves against her, but she’s not locked into a bad deal if things go well.
Example 2: Jerome the Retail Trader
Jerome is a small-time trader who likes to predict stock prices. He uses tradevision.io to analyze trends, and it tells him that a stock called (let’s say) ADVN is likely to drop in price next month. To profit from this prediction, Jerome buys a put option on ADVN. Here’s what happens:
- If the stock price drops below the strike price, Jerome can buy the stock at the lower market price and sell it at the higher strike price, making a profit.
- If the stock price goes up instead, Jerome doesn’t have to do anything. He just loses the small amount he paid for the option.
This is a low-risk way for Jerome to bet on a stock’s price movement without having to buy the stock itself.
Key Takeaways
- Options are contracts that give you the right to buy or sell something at a specific price and date.
- Call options let you buy, while put options let you sell.
- Options can be used for insurance (protecting against losses) or speculation (betting on price movements).
- European options can only be used on the expiration date, not before.
- Whether you’re a business owner like Nancy or a trader like Jerome, options can be a useful tool to manage risk or make money.
Final Thought
Options might seem intimidating at first, but they’re just another tool in the financial toolbox. Whether you’re protecting your business from currency fluctuations or making smart trades in the stock market, understanding options can open up new opportunities. And who knows? Maybe you’ll be the next Nancy or Jerome, using options to your advantage!