Options trading can seem daunting to many investors due to its complexity and the multitude of strategies available. However, understanding and applying effective option strategies can significantly enhance your trading performance and help you manage risk. In this article, we’ll delve into some of the most effective option strategies, breaking them down into actionable insights to aid both novice and experienced traders.
Understanding Options Basics
Before diving into strategies, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of options:
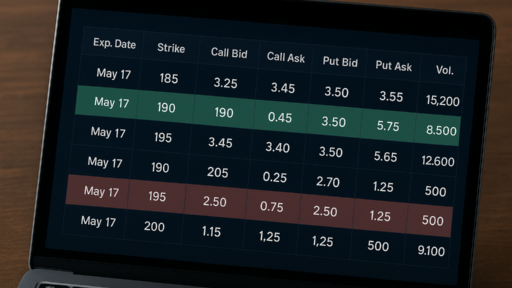
- Call Options: These give the holder the right (but not the obligation) to buy an asset at a specified strike price before a certain date.
- Put Options: These give the holder the right (but not the obligation) to sell an asset at a specified strike price before a certain date.
- Premium: The cost of purchasing an option.
- Strike Price: The price at which the asset can be bought or sold.
- Expiration Date: The last date the option can be exercised.
Effective Option Strategies
1. Covered Call
What It Is:
A covered call involves owning the underlying asset and selling a call option on that asset.
How It Works:
- Example: Suppose you own 100 shares of XYZ stock, trading at $50 per share. You sell a call option with a strike price of $55.
- Potential Outcome: If the stock price remains below $55, you keep the premium from the option sale and retain your shares. If it exceeds $55, you sell your shares at the strike price, potentially profiting from both the premium and capital gains.
Benefits:
- Generates additional income from the premium.
- Provides a small cushion against potential losses in the underlying asset.
Risks:
- Limited upside potential since the shares may be called away at the strike price.
- You may miss out on significant gains if the asset’s price surges.
2. Protective Put
What It Is:
A protective put involves holding a long position in an asset and buying a put option on that asset.
How It Works:
- Example: You own 100 shares of ABC stock at $70. To hedge against a potential drop, you buy a put option with a strike price of $65.
- Potential Outcome: If the stock price falls below $65, you can sell your shares at the strike price, limiting your losses.
Benefits:
- Provides downside protection.
- Allows you to participate in potential upside gains while limiting losses.
Risks:
- Cost of purchasing the put option, which can add up if frequently used.
- If the asset’s price rises, the cost of the put option can reduce overall profits.
3. Iron Condor
What It Is:
An iron condor is a neutral strategy that involves four options contracts: selling one call and one put, and buying another call and put at different strike prices.
How It Works:
- Example: You sell a call option at a $55 strike price and buy another call option at a $60 strike price. Simultaneously, sell a put option at a $45 strike price and buy another put option at a $40 strike price.
- Potential Outcome: You profit if the underlying asset remains within the range defined by the strike prices of the sold options.
Benefits:
- Generates profit from minimal price movement.
- Limited risk and reward, which makes it suitable for markets with low volatility.

Risks:
- Profit potential is capped.
- Requires the underlying asset to stay within a specific range.
4. Straddle
What It Is:
A straddle involves buying both a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
How It Works:
- Example: Buy a call and a put option for XYZ stock, both with a $50 strike price.
- Potential Outcome: Profit from significant price movement in either direction. If the stock price moves significantly above or below $50, the gains from one option can outweigh the cost of both options.
Benefits:
- Benefits from high volatility.
- No need to predict the direction of the price movement.
Risks:
- Requires significant price movement to cover the cost of both options.
- Can be expensive due to the cost of purchasing both call and put options.
Key Considerations
1. Market Conditions:
- Volatility: Some strategies thrive in high volatility (e.g., straddles), while others perform better in stable markets (e.g., iron condors).
- Trend Analysis: Understanding the market trend can help select the most suitable strategy.
2. Risk Tolerance:
- Evaluate your comfort level with potential losses and gains. Protective puts and covered calls are generally more conservative, while straddles involve higher risk.
3. Cost:
- Consider the premiums and potential transaction fees associated with each strategy. Some strategies, like straddles, can be costly.
4. Investment Goals:
- Align strategies with your broader investment objectives, whether it’s generating income, hedging risk, or speculating on price movements.
Conclusion
Effective option strategies can be powerful tools for enhancing returns and managing risk in your investment portfolio. By understanding the basics and applying strategies like covered calls, protective puts, iron condors, and straddles, you can navigate different market conditions with greater confidence. Remember to carefully assess your risk tolerance, market conditions, and investment goals to choose the most suitable strategy. As with any trading strategy, continuous learning and practice are key to becoming proficient in options trading.